Introduction to Elliott Wave Impulses
The Elliott Wave Principle, developed by Ralph Nelson Elliott in the 1930s, is a powerful technical analysis tool used to forecast market trends by identifying repetitive price patterns, or “waves.” Among these patterns, the impulse wave is the cornerstone of the Elliott Wave Theory, representing the dominant direction of the market trend. Impulse waves move in the direction of the larger trend, whether bullish or bearish, and are characterized by a five-wave structure. This page explores the structure, rules, and significance of impulse waves, providing insights for traders and investors.
What is an Impulse Wave?
An impulse wave is a motive wave that drives the market in the direction of the primary trend. It consists of five sub-waves, labeled 1-2-3-4-5, where waves 1, 3, and 5 are impulsive (moving with the trend), and waves 2 and 4 are corrective (moving against the trend). These waves adhere to specific rules that ensure their validity, making them distinguishable from other wave patterns. Impulse waves can appear in various timeframes, from intraday charts to multi-year cycles, reflecting the fractal nature of markets.
A typical impulse wave structure with five sub-waves (1-2-3-4-5). Source: Elliott Wave International.
Rules of Impulse Waves
To be classified as a valid impulse wave, the pattern must follow three strict rules:
- Wave 2 must not retrace more than 100% of Wave 1: This ensures that the corrective wave does not negate the initial impulsive move.
- Wave 3 cannot be the shortest of Waves 1, 3, and 5: Wave 3 is often the longest and most powerful, reflecting strong market momentum.
- Waves 1 and 4 must not overlap: The price range of Wave 4 should not enter the price territory of Wave 1, except in rare diagonal patterns.
Additionally, impulse waves typically exhibit a sub-wave structure where waves 1, 3, and 5 are composed of five smaller waves, and waves 2 and 4 consist of three corrective waves (labeled a-b-c). These rules help traders identify and validate impulse patterns in real-time market analysis.
Types of Impulse Waves
Impulse waves can manifest in different forms, each with unique characteristics:
- Regular Impulse: The standard five-wave pattern with clear adherence to the three rules. It is the most common form and indicates a strong trend.
- Extended Impulse: One of the impulsive waves (usually Wave 3 or 5) is significantly longer than the others, reflecting exaggerated market momentum.
- Truncated Fifth Wave: A rare pattern where Wave 5 fails to extend beyond the end of Wave 3, often signaling trend exhaustion.

An extended impulse wave with an elongated Wave 3. Source: Elliott Wave International.
Applying Impulse Waves in Trading
Impulse waves are critical for traders as they signal the direction of the larger trend, offering opportunities to enter trades with the trend. For example, a trader identifying an upward impulse wave may go long during Wave 3, the strongest phase, and exit or short the market as Wave 5 completes, anticipating a corrective wave. Combining impulse wave analysis with Fibonacci retracement levels (e.g., 38.2% or 61.8% for Wave 2 and 4 retracements) enhances precision in entry and exit points.
To apply impulse waves effectively:
- Identify the Trend: Determine whether the market is in a bullish or bearish impulse phase using higher-degree charts.
- Count Waves: Start from the end of a corrective wave to count the five sub-waves of an impulse, ensuring compliance with the three rules.
- Use Indicators: Combine with tools like the Elliott Wave Oscillator or moving averages to confirm wave counts and momentum.

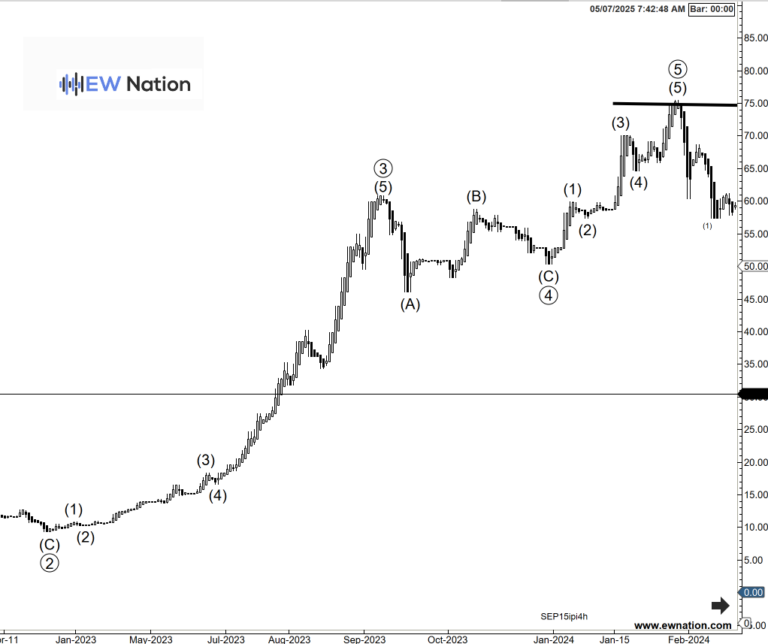
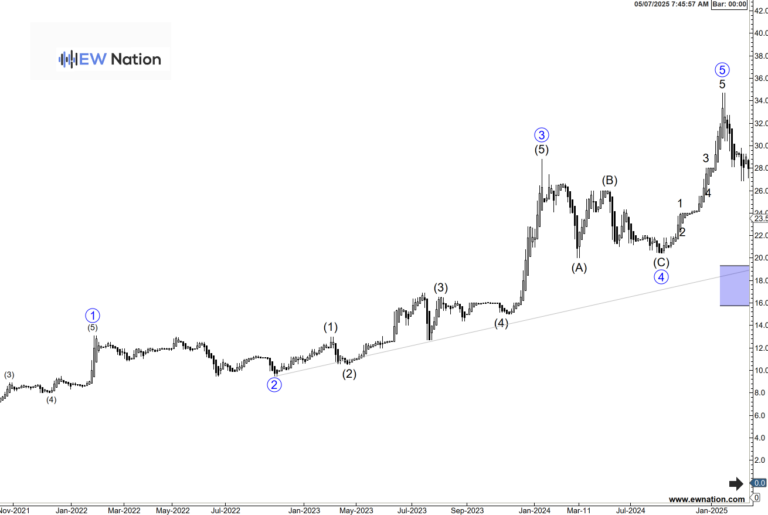
A real-world example of an impulse wave in a bullish market. Source: EWNation.
Challenges and Considerations
While impulse waves are powerful, they can be challenging to identify in real-time due to market noise and subjective interpretations. Common pitfalls include miscounting waves or forcing patterns to fit preconceived notions. To mitigate these risks, always consider alternative wave counts and use larger timeframes to contextualize the pattern within the broader trend. Patience and discipline are essential, as premature entries or exits can lead to losses.
Learn More with EWNation
Mastering impulse waves is a vital step in becoming proficient in Elliott Wave analysis. At EWNation, we offer comprehensive resources, including video courses, premium analyses, and real-time market forecasts, to help you apply these patterns effectively. Explore our Education Section to deepen your understanding and elevate your trading skills.
